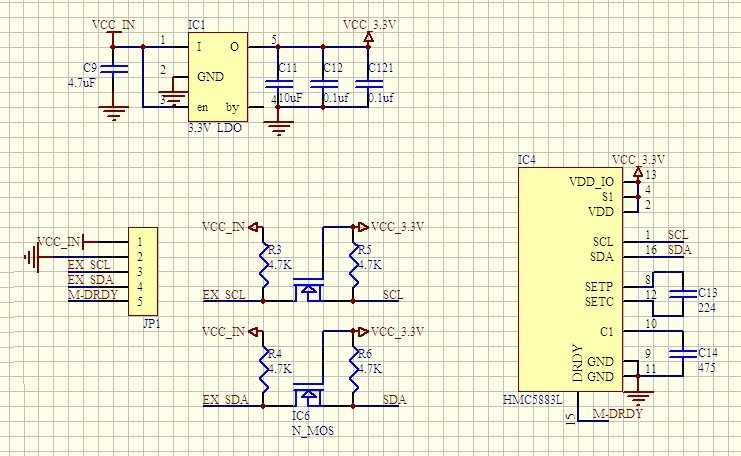
GY-271 HMC5883L 3-Axis Magnetic Electronic Compass Module
Contents
[hide]Introduction
The Compass Module is designed for low-field magnetic sensing with a digital interface and perfect to give precise heading information. This compact sensor fits into small projects such as UAVs and robot navigation systems. The sensor converts any magnetic field to a differential voltage output on 3 axes. This voltage shift is the raw digital output value, which can then be used to calculate headings or sense magnetic fields coming from different directions.
Main Features
- Gold plating PCB, applying machine welding technology, superb technique and reliably quality guarantee!
- Name: HMC5883L Module (Triaxial Magnetic Field Module);
- Type: GY-271;
- Used Chip: HMC5883L;
- Power Supply: 3~5V;
- Communication Mode: Standard IIC communicating protocol;
- Measuring Range: ±1.3-8 Gauss.
Introduction of Pins
| Pin Introduction | |
|---|---|
| VCC | Connected to the anode of the power supply (3~5v) |
| GND | Connected to the cathode of the power supply |
| SCL | I²C clock |
| SDA | I²C data |
| DRDY | Interrupting pin for data preparation, DRDY is pulled up inside and keeps the low level for 250μsec when the data are on the output register. |
Principle
Honeywell HMC5883L is a kind of SMT High integration module that has a weakly magnetic sensor chip with digital interface. It is widely used in testing of low cost compass and magnetic field. HMC5883L contains the latest high resolution HMC118X series magnetoresistive sensor and Honeywell-patent integrated circuit including amplifier, automatic demagnetization driver, deviation calibration and 12-bit A/D converter that can keep the precision of compass ranging within 1°~2°. What’s more, it has simply equipped I2C series bus interfaces.
Experimental Procedures for Arduino
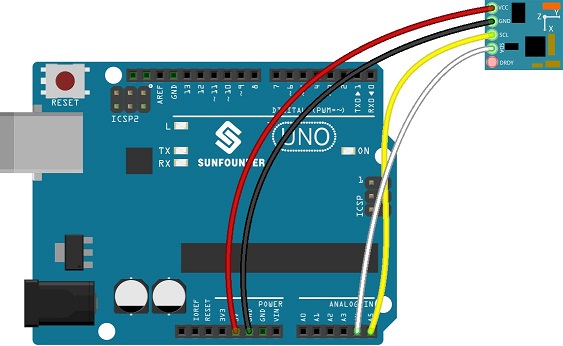
| GY-271 | Arduino uno |
| VCC | VCC |
| GND | GND |
| SCL | A5 |
| SDA | A4 |
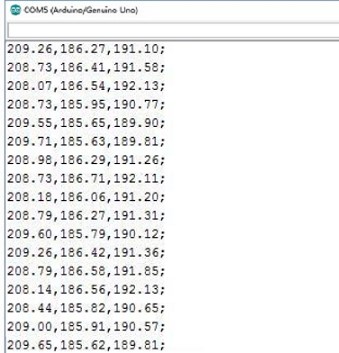
The serial monitor shows the results (X plane angle, Y plane angle, Z plane angle in degrees) of different positions of the module.
Step 2: Compile and upload the code.
/*
* HMC5883L Demo.
* dipmicro electronics, 2014
*
* Hardware Used:
*
* Arduino UNO or compatible
* GY271 module (dipmicro part DE4196
* Arduino GND -> GY271/HMC5883L GND
* Arduino 3.3V -> GY271/HMC5883L VCC
* Arduino A4 (SDA) -> GY271/HMC5883L SDA
* Arduino A5 (SCL) -> GY271/HMC5883L SCL
*/
#include <Wire.h> //I2C Arduino Library
#define HMC5883L_ADDR 0x1E //0011110b, I2C 7bit address of HMC5883
bool haveHMC5883L = false;
bool detectHMC5883L ()
{
// read identification registers
Wire.beginTransmission(HMC5883L_ADDR); //open communication with HMC5883
Wire.write(10); //select Identification register A
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(HMC5883L_ADDR, 3);
if(3 == Wire.available()) {
char a = Wire.read();
char b = Wire.read();
char c = Wire.read();
if(a == 'H' && b == '4' && c == '3')
return true;
}
return false;
}
void setup()
{
//Initialize Serial and I2C communications
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("GY271 TEST");
Wire.begin();
// lower I2C clock http://www.gammon.com.au/forum/?id=10896
TWBR = 78; // 25 kHz
TWSR |= _BV (TWPS0); // change prescaler
}
void loop()
{
bool detect = detectHMC5883L();
if(!haveHMC5883L)
{
if(detect)
{
haveHMC5883L = true;
Serial.println("We have HMC5883L, moving on");
// Put the HMC5883 IC into the correct operating mode
Wire.beginTransmission(HMC5883L_ADDR); //open communication with HMC5883
Wire.write(0x02); //select mode register
Wire.write(0x00); //continuous measurement mode
Wire.endTransmission();
}
else
{
Serial.println("No HMC5883L detected!");
delay(2000);
return;
}
}
else
{
if(!detect) {
haveHMC5883L = false;
Serial.println("Lost connection to HMC5883L!");
delay(2000);
return;
}
}
int x,y,z; //triple axis data
//Tell the HMC5883 where to begin reading data
Wire.beginTransmission(HMC5883L_ADDR);
Wire.write(0x03); //select register 3, X MSB register
Wire.endTransmission();
//Read data from each axis, 2 registers per axis
Wire.requestFrom(HMC5883L_ADDR, 6);
if(6<=Wire.available()){
x = Wire.read()<<8; //X msb
x |= Wire.read(); //X lsb
z = Wire.read()<<8; //Z msb
z |= Wire.read(); //Z lsb
y = Wire.read()<<8; //Y msb
y |= Wire.read(); //Y lsb
}
//Print out values of each axis
Serial.print("x: ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(" y: ");
Serial.print(y);
Serial.print(" z: ");
Serial.println(z);
delay(250);
}
The serial monitor shows the results (X plane angle, Y plane angle, Z plane angle in degrees) of different positions of the module.