GY-33 Color Recognition Sensor Module
Contents
[hide]Introduction
GY-33 color recognition sensor module has these advantages: low cost, small volume, easy to mount, low-power consumption and its working voltage is 3~5V.

TCS347525
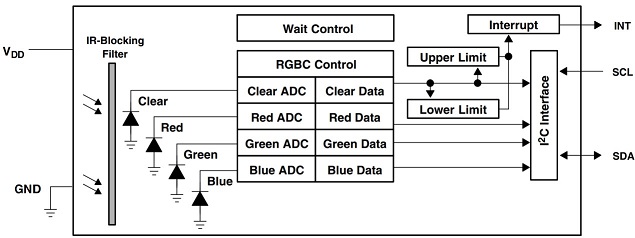
The TCS3472 device provides a digital return of red, green, blue (RGB), and clear light sensing values. An IR blocking filter, integrated on-chip and localized to the color sensing photodiodes, minimizes the IR spectral component of the incoming light and allows color measurements to be made accurately. The high sensitivity, wide dynamic range, and IR blocking filter make the TCS3472 an ideal color sensor solution for use under varying lighting conditions and through attenuating materials.
Features
- Measure Range: RGB 0~255;
- Frequency: 10 Hz;
- Working Voltage: 3~5V;
- Working Electric Current: 15mA;
- Working Temperature: -20° ~ 85°;
- Storage Temperature: -40° ~ 125°;
- Size: 24.3mm x 26.7mm;
- Sensor Chip: TCS34725.
Introduction of Pins
| Pin Introduction | |
|---|---|
| GND | Connected to the cathode of the power supply |
| DR | Serial port UART_RX/IIC_SDA |
| VCC | Connected to the anode of the power supply(3v-5v) |
| NC | Remain, do not connect to anything |
| INT | TCS34725 color chip breaks off s1=0 (wiring up GND, run it) |
| SDA | TCS34725 color chip data wire s1=0(wiring up GND, run it) |
| SCL | TCS34725 clock line of color chip s1 = 0 (wiring up GND, run it) |
| S0 | Serial/MCU_IIC Mode Choose |
| S1 | Only let sensor chip choose |
Principle
LED lights up and illuminates the detected objects. The reflected lights detect the ratio of RGB via the filter and recognize the colors according to the RGB ratio.
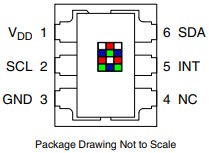
TCS347525
The TcS34725 light-to-digital converter contains a 3 X 4 photodiode array, four analog-to-digital converters (ADC) that integrate the photodiode current, data registers, a state machine, and an I2C interface. THE 3 X 4photodiode array is composed of red-filtered, green-filtered, blue-filtered, and clear (unfiltered) photodiodes. In addition, the photodiodes currents use a 16-bit digital value. Upon completion of a conversion cycle, the results are transferred to the data registers, which are double-buffered to ensure the integrity of the data. All of the internal timing, as well as the low-power wait state, is controlled by the state machine.
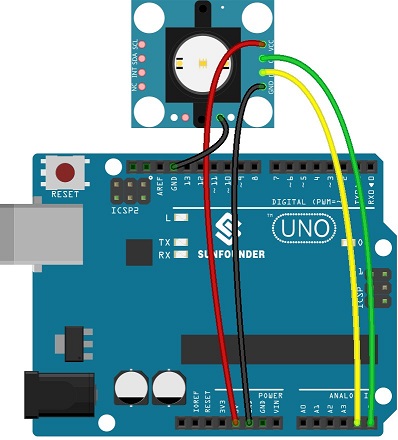
Experimental Procedures for Arduino
Step 1:Connect the circuit:
| GY-33 | Uno Board |
| VCC | VCC |
| CT | A5 |
| DR | A4 |
| GND | GND |
| SO | GND |
Step 2: Compile and upload the code.
/****************************************/
#include <i2cmaster.h>
#define uint16_t unsigned int
typedef struct
{
uint16_t Red;
uint16_t Green;
uint16_t Blue;
uint16_t Clear;
} RGB;
unsigned char Re_buf;
unsigned char sign=0;
RGB rgb;
uint16_t CT=0,Lux=0;
byte color=0,rgb_data[3]={0};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
i2c_init();
delay(1);
}
void loop() {
unsigned char data[9]={0};
if(!sign)
{
iic_read(0x00,data,8);
rgb.Red=(data[0]<<8)|data[1];
rgb.Green=(data[2]<<8)|data[3];
rgb.Blue=(data[4]<<8)|data[5];
rgb.Clear=(data[6]<<8)|data[7];
Serial.print("Red: ");
Serial.print(rgb.Red);
Serial.print(",Green: ");
Serial.print( rgb.Green);
Serial.print(",Blue");
Serial.print( rgb.Blue);
Serial.print(",Clear");
Serial.println(rgb.Clear);
iic_read(0x08,data,4);
Lux=(data[0]<<8)|data[1];
CT=(data[2]<<8)|data[3];
Serial.print("CT:");
Serial.print(CT);
Serial.print(",Lux:");
Serial.println( Lux);
iic_read(0x0c,data,3);
rgb_data[0]=data[0];
rgb_data[1]=data[1];
rgb_data[2]=data[2];
Serial.print("r:");
Serial.print( rgb_data[0]);
Serial.print(",g:");
Serial.print( rgb_data[1]);
Serial.print(",b:");
Serial.println( rgb_data[2]);
iic_read(0x0f,data,1);
color=data[0];
Serial.print(",color:");
Serial.println( color,HEX);
}
if(sign==1)
{
iic_read(0x10,&data[8],1);
i2c_start_wait(0xb4);
i2c_write(0x10);
i2c_write(0x31);
// i2c_write((data[8]|0x01));
i2c_stop();
sign=3;
}
delay(200);
}
void iic_read(unsigned char add,unsigned char *data,unsigned char len)
{
i2c_start_wait(0xb4);
i2c_write(add);
i2c_start_wait(0xb5);
while(len-1)
{
*data++=i2c_readAck();
len--;
}
*data=i2c_readNak();
i2c_stop();
}
void serialEvent() {
while (Serial.available()) {
Re_buf=(unsigned char)Serial.read();
if (Re_buf=='a')
sign=0;
if (Re_buf=='b')
sign=1;
Re_buf=0;
}
}
<pre>