Difference between revisions of "8 Channel 5V Solid State Relay Module"
(Created page with "=='''Introduction'''== A solid state relay (SSR) is just what it sounds like; an IC that acts like a mechanical relay. They allow you to control high-voltage AC loads from low...") |
(→Resource) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
You should use matched DC power to supply electricity for the module. | You should use matched DC power to supply electricity for the module. | ||
=='''Resource'''== | =='''Resource'''== | ||
| − | [http:// | + | [http://wiki.sunfounder.cc/images/7/7d/G3MB-202PEG_datasheet.pdf G3MB-202PEG_datasheet.pdf][[File:PDF.jpg]]<br> |
| − | [http:// | + | [http://wiki.sunfounder.cc/images/6/6c/8_Solid_State_Relay_pcb.zip 8 Solid State Relay pcb][[File:ZIP.jpg]] |
Latest revision as of 06:44, 20 March 2017
Contents
Introduction
A solid state relay (SSR) is just what it sounds like; an IC that acts like a mechanical relay. They allow you to control high-voltage AC loads from lower voltage DC control circuitry.
They accomplish this by using infrared light as the ‘contact,’ a solid-state relay is really just an IR LED and a phototriac sealed up into a little box.
Solid state relays, have several advantages over mechanical relays. One such advantage is that they can be switched by a much lower voltage and at a much lower current than most mechanical relays. Also, because there’s no moving contacts, solid state relays can be switched much faster and for much longer periods without wearing out.
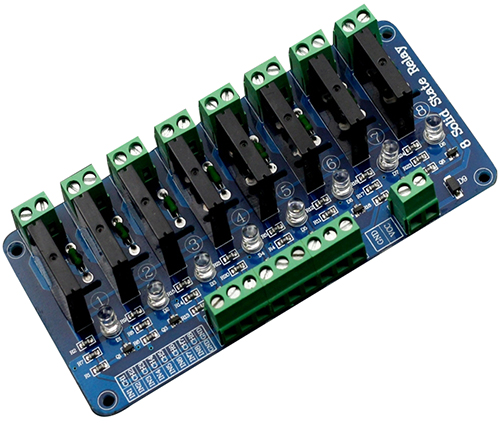
Features
- The model of solid state relay: OMRON 1565E G3MB-202P
- Size: 138 x 71 x 25mm
- Input power: 5V DC (160MA)
- Rated output load:AC100~240V 50/60Hz
- Input control signal voltage:
- (low level 0-2.5V, relay OFF)
- (high level 3-5V, relay ON)
- (low level 0-2.5V, relay OFF)
- 6. It is more convenient for the KF301 terminal to connect to control line.
- Load type: General purpose
- Isolation: Phototriac
- Zero cross: yes
- With Input resistor and built-in snubber circuit
Ports Description
Input
DC+: connected to VCC (Supply power according to relay voltage)
DC-: connected to GND
IN1: CH1 Signal triggering end of 1-channel relay module (active at high level)
IN2: CH2 Signal triggering end of 2-channel relay module (active at high level)
IN3: CH3 Signal triggering end of 3-channel relay module (active at high level)
IN4: CH4 Signal triggering end of 4-channel relay module (active at high level)
IN5: CH5 Signal triggering end of 5-channel relay module (active at high level)
IN6: CH6 Signal triggering end of 6-channel relay module (active at high level)
IN7: CH7 Signal triggering end of 7-channel relay module (active at high level)
IN8: CH8 Signal triggering end of 8-channel relay module (active at high level)
What is high level and low level?
Triggered at high level: when a forward voltage exists between signal triggering terminal (IN) and negative supply voltage. It generally connects positive supply voltage and triggering terminal together. When triggering terminal has positive supply voltage or reaches triggering voltage, the relay will close.
Triggered at low level: when the voltage between the signal triggering terminal and negative supply voltage is 0V, or the voltage at the triggering terminal is lower than positive supply voltage. If it lowers to a triggering voltage, the relay will close. It generally connects negative supply voltage and triggering terminal together.
Parameters:
| Channel | Voltage | Quiescent Current | Operating Current | Trigger Voltage | Trigger Current |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-channel | 5V | 0mA | 13.8mA | 3-5V | 2mA |
| 2-channel | 5V | 0mA | 26.8mA | 3-5V | 2mA |
| 3-channel | 5V | 0mA | 37mA | 3-5V | 2mA |
| 4-channel | 5V | 0mA | 48mA | 3-5V | 2mA |
| 5-channel | 5V | 0mA | 59mA | 3-5V | 2mA |
| 6-channel | 5V | 0mA | 70mA | 3-5V | 2mA |
| 7-channel | 5V | 0mA | 81mA | 3-5V | 2mA |
| 8-channel | 5V | 0mA | 90mA | 3-5V | 2mA |
Output Rating (Under 25℃ environmental temperature)
| Rated Load Voltage | Load Voltage Range | Load Current | Surge Current |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC100~240V 50/60Hz | AC75~264V 50/60Hz | 0.10 to 2 A | 30 A (60 Hz, 1 cycle) |
Note:
You should use matched DC power to supply electricity for the module.