Difference between revisions of "Line Follower Module"
(→Resource) |
(→Module Test) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
=='''Module Test'''== | =='''Module Test'''== | ||
'''Step 1.''' Install the Arduino IDE in your computer. For detailed steps, refer to | '''Step 1.''' Install the Arduino IDE in your computer. For detailed steps, refer to | ||
| − | <font color="blue"> | + | <font color="blue">http://wiki.sunfounder.cc/index.php?title=Install_Arduino_Software</font> |
'''Step 2.''' Connect the Arduino Uno board. | '''Step 2.''' Connect the Arduino Uno board. | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
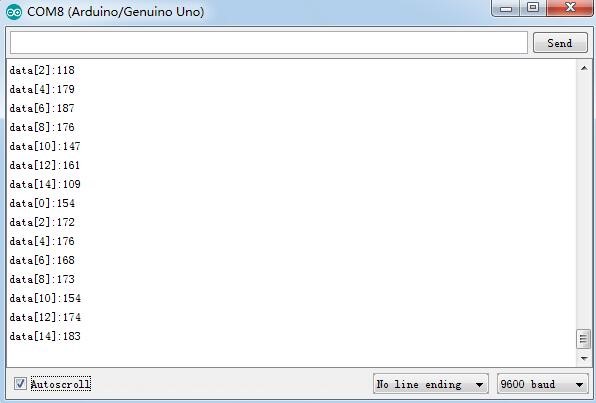
'''Step 4.''' Check the value on '''Serial Monitor.''' Click the icon [[File:LINE3.jpg]]at the right upper corner. Place the test board face down the desk and you'll see the value printed on the window as shown blow: | '''Step 4.''' Check the value on '''Serial Monitor.''' Click the icon [[File:LINE3.jpg]]at the right upper corner. Place the test board face down the desk and you'll see the value printed on the window as shown blow: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Line.jpg]] |
<font color="red">'''Note: When the module is working, it's normal to get heated.'''</font> | <font color="red">'''Note: When the module is working, it's normal to get heated.'''</font> | ||
| + | |||
=='''Resource'''== | =='''Resource'''== | ||
| − | [ | + | [http://wiki.sunfounder.cc/images/a/a8/STM8S105C4.pdf STM8S105C4 datasheet][[File:PDF.jpg]]<br> |
| − | [ | + | [http://wiki.sunfounder.cc/images/5/58/COM_SunFounder_Line_Follower_ModuleREV1.0.pdf Line Follower schematic][[File:PDF.jpg]]<br> |
| − | [ | + | [http://wiki.sunfounder.cc/images/9/9f/TCRT5000_datasheet.pdf TCRT5000_datasheet][[File:PDF.jpg]]<br> |
Latest revision as of 06:18, 20 March 2017
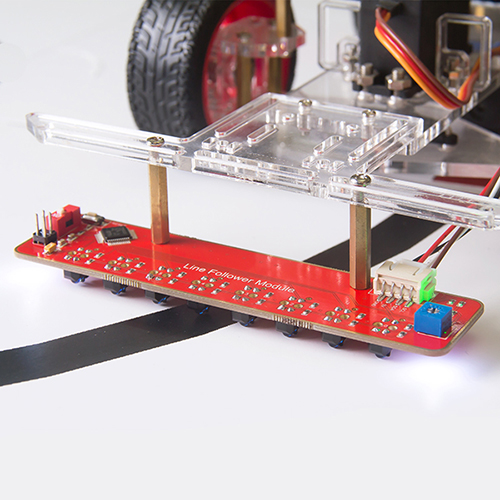
Introduction
The TCRT5000 infrared photoelectric switch adopts a high transmit power infrared photodiode and a highly sensitive phototransistor. It works by applying the principle of objects' reflecting IR light – the light is emitted, then reflected, and sensed by the synchronous circuit. Then it determines whether there exists an object or not by the light intensity. It can easily identify black and white lines.
In other words, the different conduction levels of the phototransistor when it passes over black and white lines can generate different output voltages. Therefore, all we need to do is to collect data by the AD converter on the STM8S105C4 and then send the data to the master control board via I2C communication.
This module is an infrared tracking sensor one that uses a TRT5000 sensor. The blue LED of TRT5000 is the emission tube and after electrified it emits infrared light invisible to human eye. The black part of the sensor is for receiving; the resistance of the resistor inside changes with the infrared light received.
Module application in the line following car robot:
Features
1)Uses the MCU STM8S105C4 as the controller, and the TCRT5000 infrared photoelectric sensor on each of the 8 line-following modules
2)Adopts I2C ports which only occupies 4 pins of the MCU
3)The sensor TRT5000 is highly sensitive with reliable performance
4)With a RESET button on the board for resetting, and positioning holes on the board for easy assembly
5)Supply Voltage: 5V; PCB Dimensions: 124mm x 30mm
Module Test
Step 1. Install the Arduino IDE in your computer. For detailed steps, refer to http://wiki.sunfounder.cc/index.php?title=Install_Arduino_Software
Step 2. Connect the Arduino Uno board.
Wiring:
- Test board ---- Arduino UNO
- VCC ----- 5V
- GND ----- GND
- SCL ----- A5
- SDA ----- A4
- Test board ---- Arduino UNO
After the circuit is energized, the power indicator LED D0 will brighten.
Step 3. Upload the sketch. Copy the following code to arduino IDE , before clicking the Upload (right arrow button) icon, set the Port and Board under Tools menu.
Test Code
#include <Wire.h>
#define uchar unsigned char
uchar t;
//void send_data(short a1,short b1,short c1,short d1,short e1,short f1);
uchar data[16];
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
t = 0;
}
void loop()
{
Wire.requestFrom(9, 16); // request 16 bytes from slave device #9
while (Wire.available()) // slave may send less than requested
{
data[t] = Wire.read(); // receive a byte as character
if (t < 15)
t++;
else
t = 0;
}
Serial.print("data[0]:");
Serial.println(data[0]);
Serial.print("data[2]:");
Serial.println(data[2]);
Serial.print("data[4]:");
Serial.println(data[4]);
Serial.print("data[6]:");
Serial.println(data[6]);
Serial.print("data[8]:");
Serial.println(data[8]);
Serial.print("data[10]:");
Serial.println(data[10]);
Serial.print("data[12]:");
Serial.println(data[12]);
Serial.print("data[14]:");
Serial.println(data[14]);
delay(500);
}
Step 4. Check the value on Serial Monitor. Click the icon ![]() at the right upper corner. Place the test board face down the desk and you'll see the value printed on the window as shown blow:
at the right upper corner. Place the test board face down the desk and you'll see the value printed on the window as shown blow:
Note: When the module is working, it's normal to get heated.
Resource
STM8S105C4 datasheet![]()
Line Follower schematic![]()
TCRT5000_datasheet![]()