Difference between revisions of "RGB LED Module"
(→Resource) |
(→Overview) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=='''Overview'''== | =='''Overview'''== | ||
| − | [[File:Rgb1.jpg]]<br> | + | [[File:Rgb1.jpg]][[File:RGB LED Model(witch).jpg]]<br> |
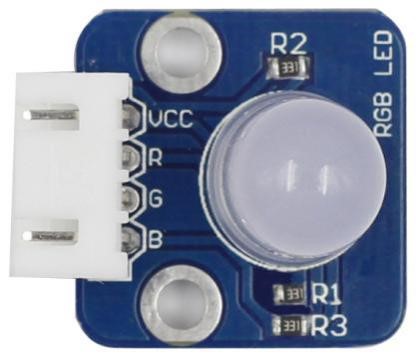
RGB LED modules can emit various colors of light. They are manufactured by packaging three LEDs of red, green, and blue into a transparent or semitransparent plastic shell and have four pins. The three primary colors, red, green, and blue, can be mixed and compose all kinds of colors by brightness, so you can make an RGB LED emit colorful light by controlling the circuit.<br> | RGB LED modules can emit various colors of light. They are manufactured by packaging three LEDs of red, green, and blue into a transparent or semitransparent plastic shell and have four pins. The three primary colors, red, green, and blue, can be mixed and compose all kinds of colors by brightness, so you can make an RGB LED emit colorful light by controlling the circuit.<br> | ||
The schematic diagram of the module is as follows:<br> | The schematic diagram of the module is as follows:<br> | ||
[[File:Rgb2.png]]<br> | [[File:Rgb2.png]]<br> | ||
RGB LEDs can be categorized into common anode LED and common cathode LED. In this module, we use a common anode RGB LED.<br> | RGB LEDs can be categorized into common anode LED and common cathode LED. In this module, we use a common anode RGB LED.<br> | ||
| + | |||
=='''Using PWM Control RGB LED'''== | =='''Using PWM Control RGB LED'''== | ||
Pulse Width Modulation, or PWM, is a technique for getting analog results with digital means. Digital control is used to create a square wave, a signal switched between on and off. This on-off pattern can simulate voltages in between full on (3.3 Volts) and off (0 Volts) by changing the portion of the time the signal spends on versus the time that the signal spends off. The duration of "on time" is called the pulse width. To get varying analog values, you change, or modulate, that pulse width. If you repeat this on-off pattern fast enough with an LED for example, the result is as if the signal is a steady voltage between 0 and 3.3v controlling the brightness of the LED.<br> | Pulse Width Modulation, or PWM, is a technique for getting analog results with digital means. Digital control is used to create a square wave, a signal switched between on and off. This on-off pattern can simulate voltages in between full on (3.3 Volts) and off (0 Volts) by changing the portion of the time the signal spends on versus the time that the signal spends off. The duration of "on time" is called the pulse width. To get varying analog values, you change, or modulate, that pulse width. If you repeat this on-off pattern fast enough with an LED for example, the result is as if the signal is a steady voltage between 0 and 3.3v controlling the brightness of the LED.<br> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:33, 10 September 2019
Overview

RGB LED modules can emit various colors of light. They are manufactured by packaging three LEDs of red, green, and blue into a transparent or semitransparent plastic shell and have four pins. The three primary colors, red, green, and blue, can be mixed and compose all kinds of colors by brightness, so you can make an RGB LED emit colorful light by controlling the circuit.
The schematic diagram of the module is as follows:

RGB LEDs can be categorized into common anode LED and common cathode LED. In this module, we use a common anode RGB LED.
Using PWM Control RGB LED
Pulse Width Modulation, or PWM, is a technique for getting analog results with digital means. Digital control is used to create a square wave, a signal switched between on and off. This on-off pattern can simulate voltages in between full on (3.3 Volts) and off (0 Volts) by changing the portion of the time the signal spends on versus the time that the signal spends off. The duration of "on time" is called the pulse width. To get varying analog values, you change, or modulate, that pulse width. If you repeat this on-off pattern fast enough with an LED for example, the result is as if the signal is a steady voltage between 0 and 3.3v controlling the brightness of the LED.
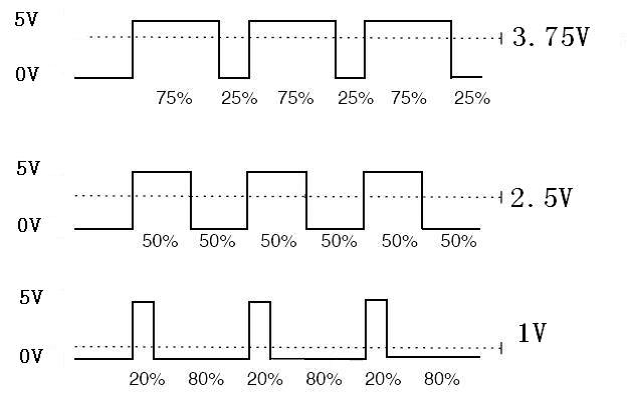
We can see from the oscillogram above that the amplitude of DC voltage output is 5V. However, the actual voltage output is only 3.75V through PWM, for the high level only takes up 75% of the total voltage within a period.
Here are the three basic parameters of PWM:
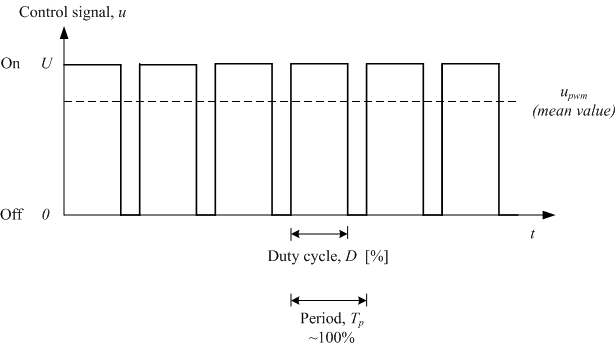
1. The term duty cycle describes the proportion of "on" time to the regular interval or "period" of time
2. Period describes the reciprocal of pulses in one second.
3. The voltage amplitude is 0V-5V.
Here we input any value between 0 and 255 to the three pins of the RGB LED to make it display different colors.
Features
1)Use a plug-in full-color common-anode RGB LED
2)A 330ohm current-limiting resistor is connected to each pin of the RGB to protect the LED from burning.
3)Adopt PWM technology to mix the three primary colors and obtain various colors
4)Working voltage: 3.3-5V DC; PCB size: 2.0 x 2.0 cm
Resource
Test Experiment for Raspberry Pi![]()
Test Experiment for Arduino![]()